Page 26 - ELG1903 Mar-Apr Issue 464
P. 26
IATEFL special .
Instructions for r
Instructions for reducing cognitive educing cognitive
load to incr
load to increase ease language learninglanguage learning
Time to put cognitive load theory on the ELT agenda? Gill Ragsdale explains
how it can help low level learners.
Another helpful process is rehearsal, which
WIKIMEDIA extends the time information spends in
working memory. Who hasn’t tried to hold
a phone number in their mind by constantly
repeating it to themselves while looking
for either a phone or a pen and paper?
This rehearsal is important in holding and
processing the information in working memory
long-enough to move it into long-term storage.
Psychologists used to think that the road
to long-term memory was a one-way-street,
but we now know that there is a lot of cross-
talk between long-term and working memory.
Unlike working memory, the information storage
capacity of long-term memory is effectively
infinite – no upper limit has been found.
A central idea in cognitive load theory,
with major consequences for education,
is that the strain on working memory (the
cognitive load) can be relieved by accessing
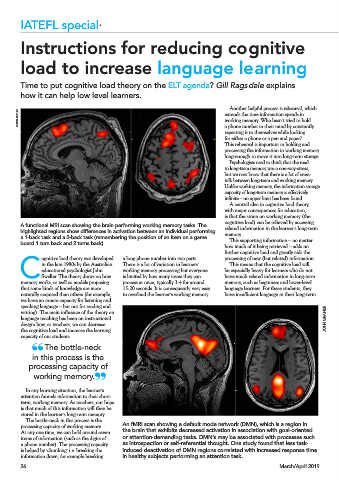
A functional MRI scan showing the brain performing working memory tasks. The related information in the learner’s long-term
highlighted regions show differences in activation between an individual performing memory.
a 1-back task and a 2-back task (remembering the position of an item on a game This supporting information – no matter
board 1 turn back and 2 turns back).
how much of it being retrieved – adds no
further cognitive load and greatly aids the
ognitive load theory was developed a long phone number into two parts. processing of new (but related) information.
in the late 1980s by the Australian There is a lot of variation in learners’ This means that the cognitive load will
educational psychologist John working memory processing but everyone be especially heavy for learners who do not
CSweller. The theory draws on how is limited by how many items they can have much related information in long-term
memory works, as well as models proposing process at once, typically 3-4 for around memory, such as beginners and lower-level
that some kinds of knowledge are more 15-20 seconds. It is consequently very easy language learners. For these students, they
naturally acquired than others (for example, to overload the learner’s working memory. have insufficient language in their long-term
we have an innate capacity for listening and
speaking language – but not for reading and
writing). The main influence of the theory on
language teaching has been on instructional JOHN GRANER
design: how, as teachers, we can decrease
the cognitive load and increase the learning
capacity of our students.
The bottle-neck
in this process is the
processing capacity of
working memory.
In any learning situation, the learner’s
attention funnels information to their short-
term, working memory. As teachers, our hope
is that much of this information will then be
stored in the learner’s long-term memory.
The bottle-neck in this process is the
processing capacity of working memory. An fMRI scan showing a default mode network (DMN), which is a region in
At any one time, we can hold around seven the brain that exhibits decreased activation in association with goal-oriented
items of information (such as the digits of or attention-demanding tasks. DMN’s may be associated with processes such
a phone number). The processing capacity as introspection or self-referential thought. One study found that less task-
is helped by ‘chunking’ i.e. breaking the induced deactivation of DMN regions correlated with increased response time
information down, for example breaking in healthy subjects performing an attention task.
26 March/April 2019